Folding Knife Mechanisms Explained: Comparing Lockbacks, Liner Locks, and Frame Locks
- Posted on

Modern folding knives employ sophisticated engineering to create locks that withstand tremendous forces while maintaining smooth operation through thousands of cycles. The evolution of locking mechanisms reflects ongoing innovation in materials, manufacturing precision, and understanding of the mechanical stresses that folding knives experience during real-world use.
Understanding folding knife locking mechanisms is crucial for selecting tools that provide reliable safety and performance in your intended applications. The locking system represents the heart of any folding knife, determining how securely the blade stays open during use and how safely it can be closed when the task is complete. Each mechanism type offers distinct advantages and limitations that directly impact user experience, safety, and long-term reliability.
Modern folding knives employ sophisticated engineering to create locks that withstand tremendous forces while maintaining smooth operation through thousands of cycles. The evolution of locking mechanisms reflects ongoing innovation in materials, manufacturing precision, and understanding of the mechanical stresses that folding knives experience during real-world use.
The Critical Importance of Locking Mechanisms
Folding knife locks serve multiple essential functions beyond simply holding the blade open. They must provide consistent engagement that users can verify by feel and sound, resist accidental disengagement during normal use, and allow controlled blade closure when desired. The lock strength must match or exceed the forces generated during cutting tasks while maintaining smooth operation that doesn't require excessive force or complex manipulation.
Safety considerations make locking mechanism selection particularly important for users who rely on their folding knives for critical tasks. A failed lock can result in serious injury when the blade unexpectedly closes during use, making reliability the paramount concern in mechanism evaluation. Understanding how different locks achieve their strength and reliability helps users select appropriate mechanisms for their specific applications and risk tolerance.
Lock engagement feedback helps users confirm proper blade deployment before committing to cutting tasks. Quality mechanisms provide distinct tactile and auditory confirmation when properly engaged, while inferior designs may offer ambiguous feedback that creates uncertainty about lock status. This positive engagement feedback becomes particularly important in low-light conditions or high-stress situations where visual confirmation may be difficult.
Lockback Mechanisms: Traditional Strength and Reliability
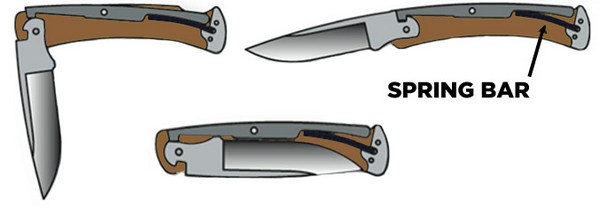
Lockback mechanisms represent one of the oldest and most proven folding knife lock designs, utilizing a spring-loaded bar that engages a notch in the blade tang to prevent closure. This time-tested design has provided reliable service for centuries, demonstrating the effectiveness of simple mechanical principles executed with precision manufacturing.
The lockback system operates through a rocker-style mechanism where a spring-loaded lock bar pivots to engage the blade tang. When the blade opens fully, the lock bar snaps into position within a notch cut into the blade tang, creating a mechanical interference that prevents the blade from closing. To release the lock, users press down on the exposed portion of the lock bar, lifting the engagement end out of the tang notch and allowing controlled blade closure.
Strengths of Lockback Mechanisms:
Lockback locks offer exceptional strength when properly manufactured, capable of withstanding tremendous forces without failure. The large contact area between the lock bar and blade tang distributes stress effectively, creating robust engagement that resists both lateral and longitudinal forces. This strength characteristic makes lockbacks popular choices for heavy-duty applications where maximum lock security is paramount.
The positive engagement feedback of lockback mechanisms provides clear confirmation of proper lock function. Users can both feel and hear the lock snap into place, while the firm resistance to accidental disengagement provides confidence during use. The distinct release motion required to disengage the lock virtually eliminates accidental closure during normal cutting tasks.
Lockback mechanisms typically prove very durable, with simple designs that resist wear and maintain consistent function through extensive use. The robust construction and large bearing surfaces help these locks maintain their strength and reliability even after thousands of operation cycles.
Limitations and Considerations:
Lockback operation requires two-handed blade closure in most designs, as users must depress the lock bar while controlling blade movement. This requirement can be inconvenient in situations where one-handed operation is preferred or necessary. Some users also find the lock bar pressure point uncomfortable during extended use, particularly with smaller knives where the bar may dig into the hand.
The lockback mechanism adds complexity to knife construction and may increase manufacturing costs compared to simpler alternatives. The spring system requires precise tensioning and proper heat treatment to ensure consistent function and longevity.
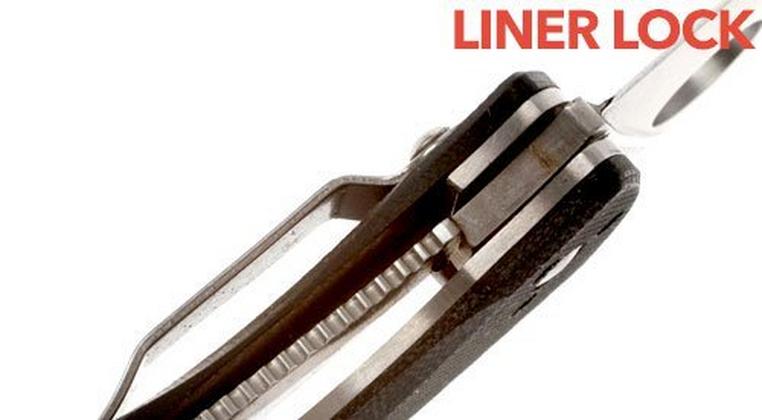
Liner Lock Systems: Lightweight Efficiency and Smooth Operation
Liner lock mechanisms utilize a thin steel liner within the handle that flexes to engage the blade tang, providing secure blade retention through spring tension and mechanical interference. This innovative design offers excellent strength-to-weight ratios while enabling smooth one-handed operation that appeals to everyday carry users.
The liner lock system operates through a steel liner positioned along one side of the handle interior. When the blade opens, the liner springs inward to engage a flat section of the blade tang, creating interference that prevents closure. To release the lock, users push the liner away from the blade tang, allowing the blade to close freely.
Advantages of Liner Lock Design:
Liner locks excel at providing one-handed operation for both opening and closing, making them highly practical for everyday carry applications where convenience and speed matter. The smooth operation and minimal force requirements make these locks comfortable for users with limited hand strength or dexterity issues.
The lightweight construction of liner locks adds minimal weight to knife designs while providing excellent strength for most applications. The thin steel liners integrate seamlessly into handle designs without requiring additional space or complex manufacturing processes.
Liner lock mechanisms typically operate very smoothly when properly manufactured, with consistent engagement and release characteristics that improve with use as the components wear into optimal contact patterns. The simple design principles make these locks relatively easy to manufacture consistently.
Potential Drawbacks:
Liner locks depend on proper spring tension for reliable function, and wear or damage to the liner can affect lock strength and reliability. Over time, repeated flexing may cause the liner to lose tension or develop stress cracks that compromise performance.
The engagement area between liner and blade tang is typically smaller than lockback designs, potentially concentrating stress in ways that could lead to premature wear or failure under extreme loads. Users who subject their knives to heavy-duty applications may find liner locks less suitable than more robust alternatives.
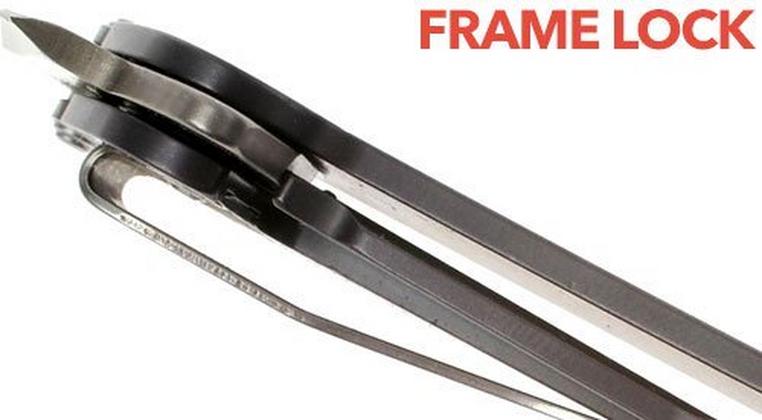
Frame Lock Mechanisms: Maximum Strength Through Integrated Design
Frame lock systems represent an evolution of liner lock principles, utilizing the actual handle frame material as the locking element rather than a separate liner. This integrated approach creates incredibly strong locks that can withstand extreme forces while maintaining the smooth operation characteristics that make them popular among both professionals and enthusiasts.
Frame locks operate by incorporating the locking function directly into one side of the handle frame, typically made from titanium, steel, or aluminum. The frame section flexes inward to engage the blade tang when opened, using the inherent strength of the handle material to provide lock security. This integration eliminates the separate liner component while creating even stronger engagement than traditional liner locks.
Benefits of Frame Lock Construction:
Frame locks offer exceptional strength that often exceeds both liner locks and many lockback designs. The substantial material thickness and robust construction create locks capable of handling extreme forces without failure, making them suitable for the most demanding applications.
The integrated design eliminates potential failure points associated with separate lock components while reducing manufacturing complexity. Frame locks typically prove extremely durable, maintaining consistent function through extensive use without the wear concerns that affect some liner lock designs.
Frame lock mechanisms provide excellent one-handed operation with positive engagement feedback that rivals lockback designs. The substantial frame material creates distinct tactile confirmation of proper lock engagement while requiring deliberate action for release.
Considerations and Limitations:
Frame lock mechanisms require precise manufacturing tolerances to ensure proper function and may be more expensive to produce than simpler alternatives. The frame material properties significantly impact lock function, with harder materials providing better wear resistance but potentially requiring more force for operation.
The thickness of frame lock mechanisms may increase overall knife dimensions compared to liner lock alternatives, potentially affecting pocket carry comfort. Some users also find that frame locks can be more difficult to operate when wearing gloves or in cold conditions where finger dexterity is reduced.
Specialized Locking Mechanisms and Modern Innovations
Beyond the three primary lock types, modern folding knives incorporate various specialized mechanisms that offer unique advantages for specific applications. Compression locks combine frame lock strength with enhanced safety features, while axis lock systems provide smooth ambidextrous operation with exceptional strength characteristics.
Button locks offer rapid deployment and secure retention through spring-loaded mechanisms that engage automatically when the blade opens. These systems typically provide excellent one-handed operation while maintaining positive lock engagement that resists accidental release.
Tri-ad lock systems utilize multiple engagement points to distribute stress and provide exceptional strength for heavy-duty applications. These specialized mechanisms often appear in tactical and rescue knives where maximum reliability is essential.
Selecting the Right Mechanism for Your Needs
Choosing the optimal locking mechanism depends on your intended use, handling preferences, and performance priorities. Understanding how different mechanisms align with specific applications helps you make informed decisions that enhance safety and user satisfaction.
For general everyday carry use, liner locks and frame locks typically provide excellent balance between convenience and reliability. The one-handed operation and smooth function make these mechanisms practical for routine tasks while providing adequate strength for normal use.
Heavy-duty applications often benefit from lockback or specialized high-strength mechanisms that provide maximum security under extreme conditions. Users who subject their knives to demanding tasks should prioritize lock strength over convenience features.
When selecting your first folding knife, understanding these mechanism differences helps you choose tools that match your skill level and intended applications. Choosing Your First Folding Knife: A Beginner's Guide to Blade Styles and Materials provides comprehensive guidance on matching all knife characteristics, including locking mechanisms, to your specific needs and preferences.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Different locking mechanisms require varying levels of maintenance to ensure continued reliable function. Understanding these requirements helps you select mechanisms that match your maintenance preferences while ensuring long-term reliability.
Lockback mechanisms typically require minimal maintenance beyond basic cleaning and occasional lubrication of pivot points. The robust construction and simple design principles make these locks relatively tolerant of neglect while maintaining function.
Liner locks benefit from periodic cleaning to remove debris that might interfere with proper engagement, along with inspection for signs of wear or damage that could affect reliability. Proper lubrication of contact points helps maintain smooth operation and reduces wear.
Frame locks require similar maintenance to liner locks but may prove more tolerant of adverse conditions due to their robust construction. Regular cleaning and inspection help ensure continued reliable function throughout the knife's service life.
Real-World Performance and User Experience
The practical implications of mechanism choice become apparent through daily use, where factors like ease of operation, reliability under stress, and long-term durability directly impact user satisfaction. Understanding how different mechanisms perform in real-world conditions helps you anticipate the ownership experience with different lock types.
Professional users often develop strong preferences based on their specific applications and operating environments. Emergency responders may prioritize locks that function reliably with gloves, while precision workers might prefer mechanisms that offer the smoothest operation and most positive control.
The versatility that quality folding knives provide depends partly on having reliable locking mechanisms that inspire confidence across diverse applications. How a Quality Folding Knife Becomes Your Most Versatile Tool explores how superior construction, including advanced locking mechanisms, enables folding knives to serve as indispensable daily tools that enhance productivity and preparedness.
Conclusion
Understanding folding knife locking mechanisms empowers you to make informed selections that prioritize safety, reliability, and performance characteristics that match your intended use. Each mechanism type offers distinct advantages that serve different user needs and application requirements.
Quality folding knives incorporate sophisticated locking mechanisms that reflect decades of engineering refinement and real-world testing. By understanding how these systems work and their respective strengths and limitations, you can select tools that provide the reliability and performance characteristics essential for safe, effective use.
The evolution of locking mechanisms continues as manufacturers develop new approaches that enhance safety, convenience, and reliability. Staying informed about these developments helps you appreciate the engineering sophistication that makes modern folding knives remarkably capable and reliable tools that serve users across countless applications and environments.
Whether you prioritize maximum strength, smooth operation, or specialized features, understanding locking mechanism principles helps you recognize quality construction and select knives that provide years of reliable service while enhancing your capability and confidence in diverse cutting tasks.



